Exploring new tokens on Base chain can be exhilarating, but it’s also a hotbed for scams and copycat contracts. Whether you’re chasing the next memecoin or evaluating a promising DeFi project, understanding Base chain contract addresses and learning how to verify them is crucial before you commit any funds.
Why Contract Address Verification Matters on Base
The rapid growth of Base has brought a surge of new tokens—some legitimate, many not. Rug pulls, fake tokens mimicking popular projects, and imposter contracts are rampant. The only way to know what you’re buying is to verify the token contract address yourself. Relying on hearsay or random Telegram links can be disastrous.

When you interact with a smart contract—whether swapping on a DEX or minting an NFT—you’re trusting code. If that code is malicious or simply isn’t what you think it is, your assets are at risk. That’s why platforms like Basescan, the official explorer for Base, emphasize contract verification as the first line of defense for users.
How to Find Official Base Token Contract Addresses
If you’re hunting for the real contract behind a trending memecoin or DeFi protocol, start with official sources:
Top Ways to Find Official Base Token Addresses
-

Check the Official Project Website: Most legitimate projects display their official contract addresses prominently on their websites. Always verify the URL to avoid phishing sites.
-

Consult the Project’s Verified Social Media: Platforms like Twitter and Discord often share contract addresses through official, verified accounts. Look for blue checkmarks or official announcements.
-
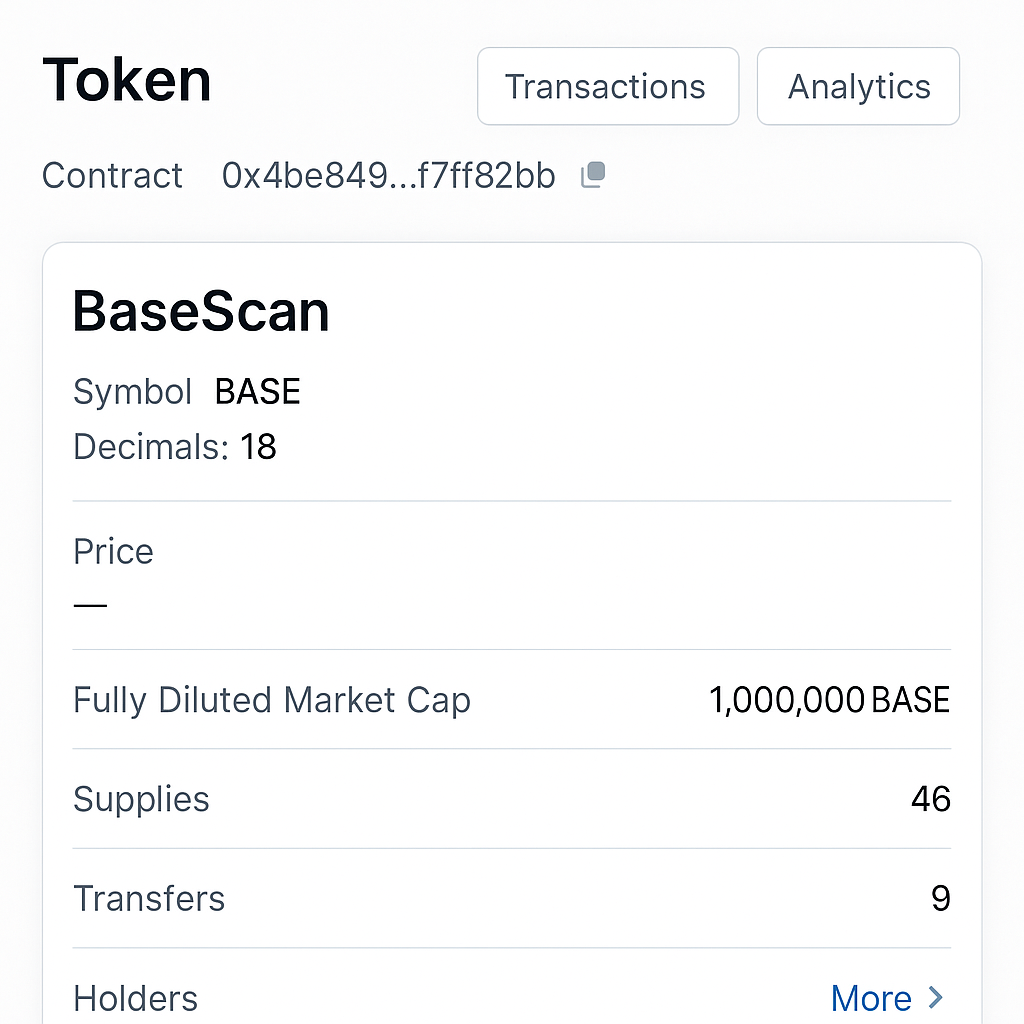
Use Reputable Blockchain Explorers: Tools like Basescan list verified contracts and token details. Search for the token and check for verification badges.
-

Check Coin Aggregator Sites: Websites such as CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap often list contract addresses for tokens, but always cross-reference with official sources.
-

Ask in Official Community Channels: If in doubt, join the project’s official Telegram or Discord and ask moderators for the correct contract address.
- Project Website: Most legitimate projects will publish their official contract address on their homepage or documentation.
- Basescan: Use Basescan’s search feature to look up tokens by name and check for verified contracts (indicated by a green checkmark).
- Official Socials: Cross-check addresses posted on the project’s verified Twitter account or Discord announcement channels.
- CEX Listings: Centralized exchanges listing Base tokens will display the correct contract address in their asset info pages.
- Dapp Aggregators: Platforms like CoinGecko and Magic Eden often list verified contract addresses for trending tokens on Base.
Avoid blindly copying addresses from random tweets, Reddit threads, or influencer posts without double-checking their authenticity. Scammers exploit FOMO by spreading fake contracts during hype cycles.
The Process: Verifying a Base Token Contract Yourself
The next step is hands-on verification. Here’s how experienced traders do it on Base:
This process usually involves checking if the source code has been published and verified (look for the green checkmark), reviewing recent transactions for suspicious activity (like massive minting or transfers to one wallet), and ensuring ownership has been renounced if it’s supposed to be community-owned.
If you want extra peace of mind, use tools like Basescan’s “Verify & Publish” feature—which allows anyone to upload source code tied to a specific address—or track ownership verification processes that require deployers to sign messages from their original wallet. This helps ensure that even if two contracts have similar names or tickers, only one is truly authentic.
Beyond just looking for the green checkmark, it pays to scrutinize the contract’s activity. Look for red flags: sudden changes in ownership, strange minting patterns, or large transfers to centralized exchanges. If you see a contract with no verified source code or a deployer address that’s linked to multiple rug pulls, steer clear.
Comparing Contracts: Spotting Fakes vs. Legitimate Tokens
Sometimes scammers will clone a popular token’s name and ticker but deploy their own malicious contract. To protect yourself:
Comparison of Verified vs Unverified Base Token Contracts
| Feature | Verified Contract ✅ | Unverified Contract ⚠️ |
|---|---|---|
| Source Code Available | Yes, fully accessible | No, hidden or unavailable |
| Audit Status | Often audited | Rarely audited |
| Contract Creator | Known and transparent | Often anonymous |
| Community Trust | High | Low |
| Easier to Analyze for Risks | Yes | No |
| Listing on Major Platforms | Likely | Unlikely |
| Potential for Malicious Code | Low | High |
Always compare the contract address from multiple sources before making any transaction. Don’t trust only what appears on DEXes—anyone can list a token on decentralized platforms without verification.
If you’re feeling technical, review the published source code directly on Basescan. Look for functions that allow unrestricted minting, blacklisting wallets, or draining liquidity—these are all classic scam mechanics.
Using Basescan API for Advanced Verification
For power users and developers, Basescan’s API lets you automate contract checks and even verify Solidity code uploads programmatically. Here’s a simple example of how you might use their API to check verification status:
Checking Base Chain Contract Verification with Basescan API
You can use the Basescan API to programmatically check if a Base chain contract is verified. Here’s a Python example using the `requests` library:
import requests
def is_contract_verified(api_key, contract_address):
url = "https://api.basescan.org/api"
params = {
"module": "contract",
"action": "getsourcecode",
"address": contract_address,
"apikey": api_key
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
data = response.json()
if data['status'] == '1' and data['result']:
contract_info = data['result'][0]
# If SourceCode is not empty, contract is verified
return bool(contract_info.get('SourceCode'))
return False
# Example usage
API_KEY = "YourBasescanAPIKeyHere"
CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0xYourContractAddressHere"
if is_contract_verified(API_KEY, CONTRACT_ADDRESS):
print(f"Contract {CONTRACT_ADDRESS} is verified on Basescan.")
else:
print(f"Contract {CONTRACT_ADDRESS} is NOT verified on Basescan.")
Replace `YourBasescanAPIKeyHere` and `0xYourContractAddressHere` with your actual Basescan API key and the contract address you want to check. A verified contract will have its source code available on Basescan.
This kind of automation is invaluable if you’re tracking new memecoin launches or running your own trading bots on Base.
Checklist: Before You Buy Any Base Token
By following this checklist every time you encounter a new project, you’ll drastically reduce your risk of falling victim to scams or copycat tokens on Base.
Frequently Asked Questions About Base Chain Contract Addresses
The explosion of memecoins and DeFi projects on Base isn’t slowing down—if anything, it’s accelerating. The best defense is skepticism combined with methodical verification using trusted tools like Basescan and official project channels. As always in crypto, don’t trust—verify.
[youtube_video: A video tutorial on verifying smart contracts on Basescan]