Coinbase’s Base network has quickly emerged as a pivotal Layer 2 solution for Ethereum, promising not just faster and cheaper transactions but also a robust security architecture. As the adoption of Layer 2 technologies accelerates, understanding how Base protects your assets is essential for anyone considering decentralized applications (dApps) or asset transfers on this platform. Let’s examine the key mechanisms that underpin Base’s security, and why they matter for both casual users and serious investors.
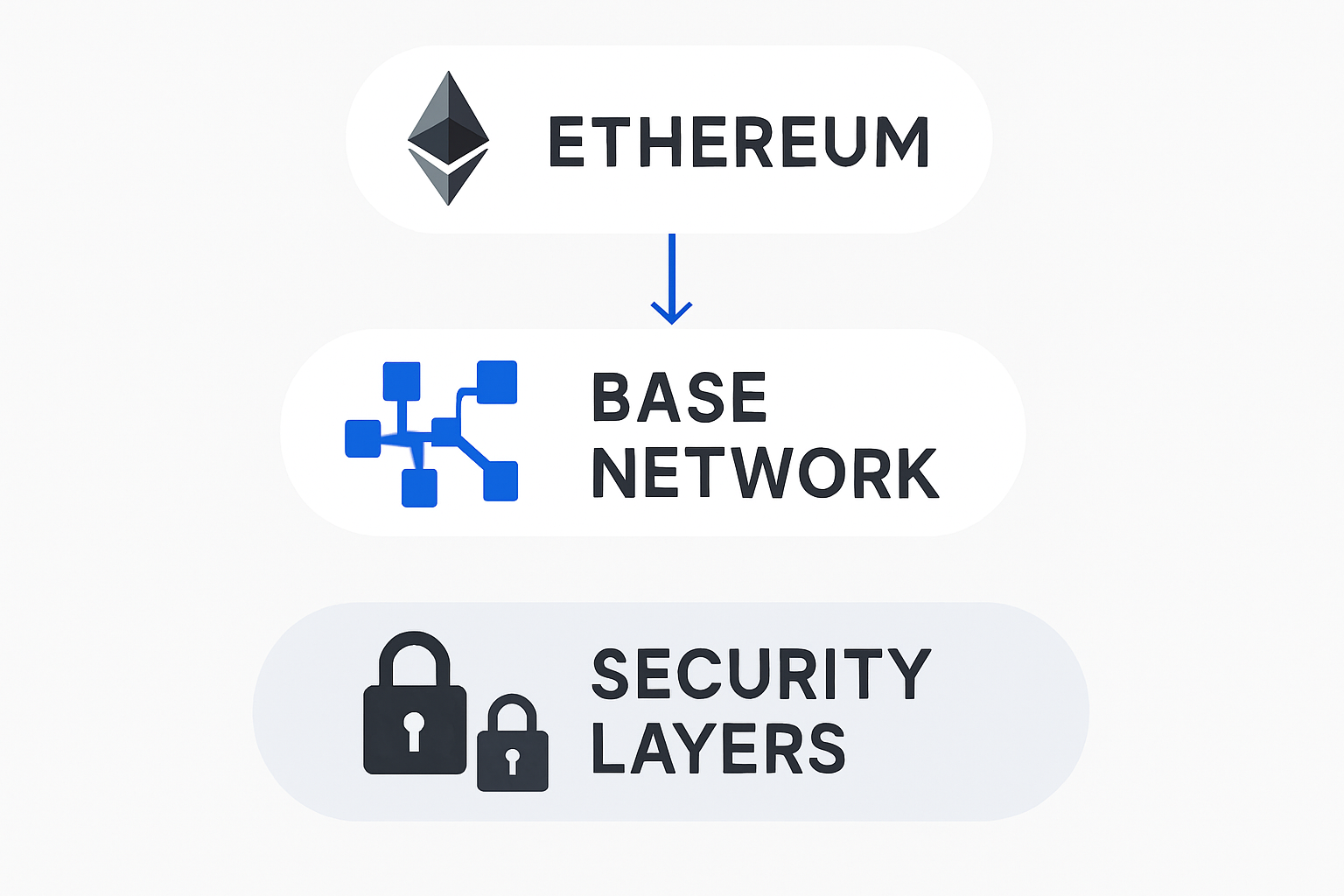
Ethereum Integration: Inheriting Security at Scale
At the heart of Base’s defense strategy is its deep integration with Ethereum. Rather than reinventing the wheel, Base operates as an extension of Ethereum, inheriting its decentralized validator set and consensus rules. This means every transaction processed on Base is ultimately anchored to Ethereum’s mainnet, providing a trustless environment where users retain full control over their funds.
This approach not only leverages Ethereum’s proven security but also ensures that asset custody remains non-custodial – you aren’t handing your coins over to a single operator or centralized entity. For developers and users alike, this reduces the risk profile significantly compared to standalone sidechains or less integrated Layer 2s.
Decentralization Efforts: The Stage 1 Rollup Leap
Centralization has long been a concern for rollups and Layer 2 protocols. In April 2025, Base achieved what’s known as ‘Stage 1’ rollup status by introducing a ten-member security council comprised of independent entities. This council is tasked with overseeing critical network upgrades and responding to emergencies, reducing the reliance on Coinbase as a single point of failure.
This move marks a significant step towards true decentralization – spreading governance power across multiple stakeholders increases resilience against coordinated attacks or insider threats. It also aligns with the broader ethos of DeFi: minimizing trust assumptions wherever possible.
Monitoring Tools and Fraud Detection: Proactive Threat Management
Security in blockchain isn’t just about fortifying walls; it’s about active surveillance for evolving threats. Base employs advanced monitoring tools like Pessimism – an automated system designed to detect real-time anomalies and flag suspicious activity before it escalates into systemic risk.
In addition to constant monitoring, sophisticated fraud-proof mechanisms are integral to Base’s architecture. These systems can identify double-spending attempts or invalid state transitions, ensuring that even if someone tries to game the system, fraudulent transactions can be detected and reversed before any damage occurs.
What sets Base apart is its layered approach to fraud prevention. While many Layer 2s rely primarily on optimistic assumptions and post-facto dispute windows, Base’s integration of real-time anomaly detection and multi-party oversight means threats are addressed proactively, not reactively. This design philosophy is crucial for building user confidence, especially as the value locked in Layer 2 networks continues to grow.
Escape Hatch Mechanism: User Empowerment in Adverse Scenarios
No system is immune to disruption, whether from technical glitches or malicious actors. Recognizing this, Base incorporates an escape hatch: a vital safety valve that allows users to withdraw their assets directly to Ethereum Layer 1 if the operator fails to process rollup blocks or propose new state roots. This mechanism ensures that even in worst-case scenarios, your funds remain accessible and under your control.
For users wary of centralized intervention or network outages, the escape hatch provides peace of mind. It’s a testament to Base’s commitment to user sovereignty, a principle that underpins the entire ethos of decentralized finance.
Balancing Efficiency with Security: What Users Should Know
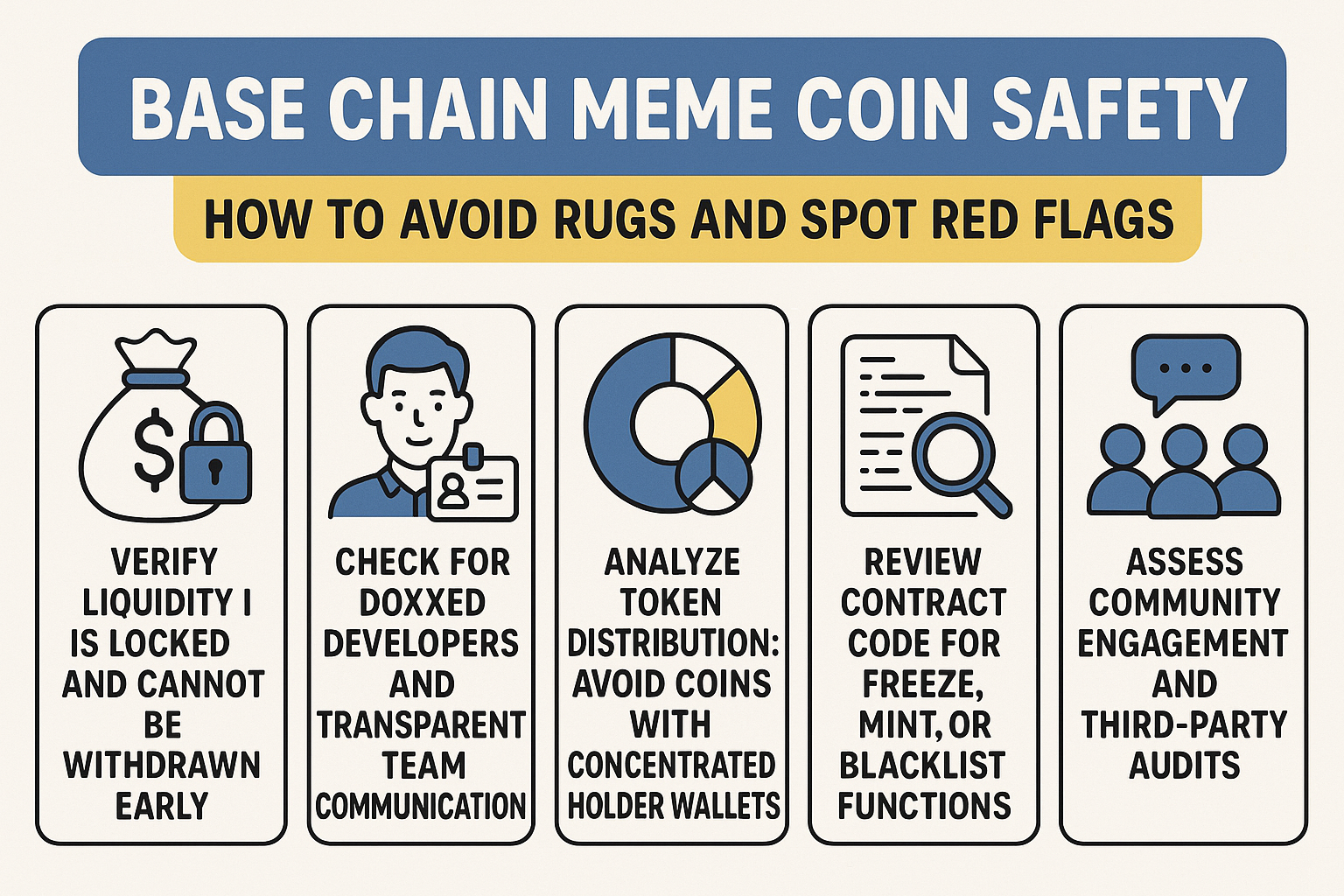
While Base’s technical safeguards are impressive, it’s important for users to understand their own role in maintaining security. Always verify contract addresses before bridging assets, use hardware wallets for large sums, and stay updated on network advisories from official channels. Remember, even the most secure protocol can’t protect against social engineering or user error.
For developers building on Base, rigorous code audits and responsible disclosure practices remain essential. The platform offers robust tools for monitoring and alerting but ultimately relies on a vigilant community to report vulnerabilities and suspicious activity.
The Road Ahead: Continuous Improvement
Security is not a static achievement, it’s an ongoing process. As usage grows and new attack vectors emerge, Base will need to continuously adapt its monitoring systems, governance structures, and emergency procedures. The recent move toward decentralization with its ten-member security council shows that Base is committed not just to short-term safety but also long-term resilience.
For investors and everyday users alike, these developments mean you’re operating on a platform that takes risk management seriously while delivering all the speed and cost benefits of Layer 2 scaling. In a landscape where trust can be fragile, Base’s multi-layered security model stands out as both pragmatic and forward-thinking.